Business Process Management (BPM)
Business process management (BPM) is defined as an approach of aligning the organization's business processes with the prerequisites of clients. BPM as a “Holistic Management” approach embedded with technology promotes business effectiveness and efficiency, while striving for innovation, flexibility. BPM attempts to improve processes continuously and therefore can be described as a "process optimization process." BPM modern management approach enables organizations to be more efficient, more effective and more capable of change resulting in generation of revenue and cut down the operational costs.
BPM visualizes processes as strategic assets of an organization that need to be understood, managed, and improved to deliver value-added products and services to clients. BPM offers an approach to integrate human and technological "change capability” of organization in a productive way.
Business process management activities are grouped into six categories: vision, design, modeling, execution, monitoring, and optimization.
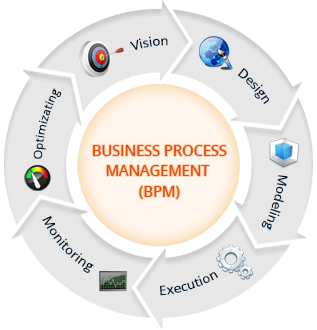
Vision
Design
Modeling
Execution
Monitoring
Optimization
Business process management (BPM) properly executed by qualified professionals has the capacity to reduce costs, enhance efficiency and productivity, and minimize errors and risk – thereby protecting and optimizing corporate resources. Implementing best practices in business process management contributes to sound financial management and provides feedback on how well an organization is succeeding in meeting its goals.
The BPM functions are planned in accordance to strategic vision and goals of an organization. Each function is attached with a list of processes.
Process Design defines the process flow, the factors within it, alerts & notifications, escalations, Standard Operating Procedures, Service Level Agreements, and task hand-over mechanisms.
Modeling takes the theoretical design and introduces combinations of variables to determine how the process might operate under different circumstances.
To automate processes, it is required to develop or purchase an application that executes the required steps of the process. Automating a process requires flexible and comprehensive infrastructure.
It involves the tracking of individual processes to view the information status at that particular stage. The degree of monitoring depends on business demands of the organization.
Process optimization includes retrieving process performance information from modeling or monitoring phase for identifying the hidden potential, opportunities for cost savings and other improvements and applying those enhancements in the design of the process.
Business process management (BPM) properly executed by qualified professionals has the capacity to reduce costs, enhance efficiency and productivity, and minimize errors and risk – thereby protecting and optimizing corporate resources. Implementing best practices in business process management contributes to sound financial management and provides feedback on how well an organization is succeeding in meeting its goals.

